
The Geography of Sri Lanka
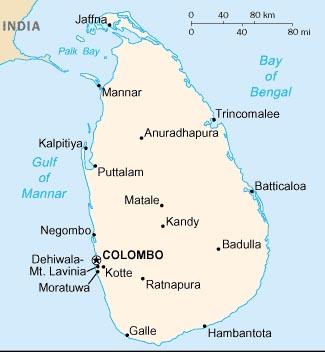
- Southern Asia, island in the Indian Ocean, south of India
- Geographic coordinates: 7 00 N, 81 00 E
- Map references: Asia
Area
- total: 65,610 sq km
- water: 870 sq km
- land: 64,740 sq km
- comparative: slightly larger than West Virginia
Boundaries
- Land boundaries: 0 km
- Coastline: 1,340 km
Maritime claims
- contiguous zone: 24 NM
- territorial sea: 12 NM
- exclusive economic zone: 200 NM
- continental shelf: 200 NM or to the edge of the continental margin
Climate
- tropical monsoon; northeast monsoon (December to March); southwest monsoon (June to October)
Terrain
- mostly low, flat to rolling plain; mountains in south-central interior
Elevation extremes
- lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m
- highest point: Pidurutalagala 2,524 m
Natural resources
- limestone
- graphite
- mineral sands
- gems
- phosphates
- clay
- hydropower
Land use
- arable land: 13.43%
- permanent crops: 15.78%
- other: 70.79% (1998 est.)
- irrigated land: 6,510 sq km (1998 est.)
Natural hazards
- occasional cyclones and tornadoes
Environment -- current issues
deforestation; soil erosion; wildlife populations threatened by poaching and urbanization; coastal degradation from mining activities and increased pollution; freshwater resources being polluted by industrial wastes and sewage runoff; waste disposal; air pollution in Colombo
Environment - international agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Marine Life Conservation
Geography - note:
strategic location near major Indian Ocean sea lanes
Source
2003 World Factbook (http://www.odci.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/ce.html)


Last Modified: 1 December 2003
![]()
